How Cultural Differences Affect the Reciprocity Principle in Marketing
The reciprocity principle in marketing is a fundamental psychological concept that influences consumer behavior across various cultures. This principle suggests that people feel compelled to return favors or kindness when they receive something. However, the manifestation of this principle can vary significantly depending on cultural contexts. In Western cultures, consumers often expect direct exchanges, seeing promotional offers as obligations to reciprocate. In contrast, Eastern cultures may perceive exchanges in a more holistic manner. Learning and acknowledging these differences is critical to developing effective marketing strategies. Marketers who understand cultural nuances can design campaigns that resonate with target audiences. For example, incorporating elements of local customs in promotional offers can enhance the perceived value in diverse markets. Additionally, marketers must consider cultural cues that trigger the reciprocity instinct, as these cues vary significantly worldwide. An effective way to engage customers is through personalized experiences that create a sense of indebtedness. Ultimately, recognizing and addressing cultural differences in the reciprocity principle leads to more effective marketing outcomes and builds stronger customer relationships, thus establishing a successful venture in a global market.
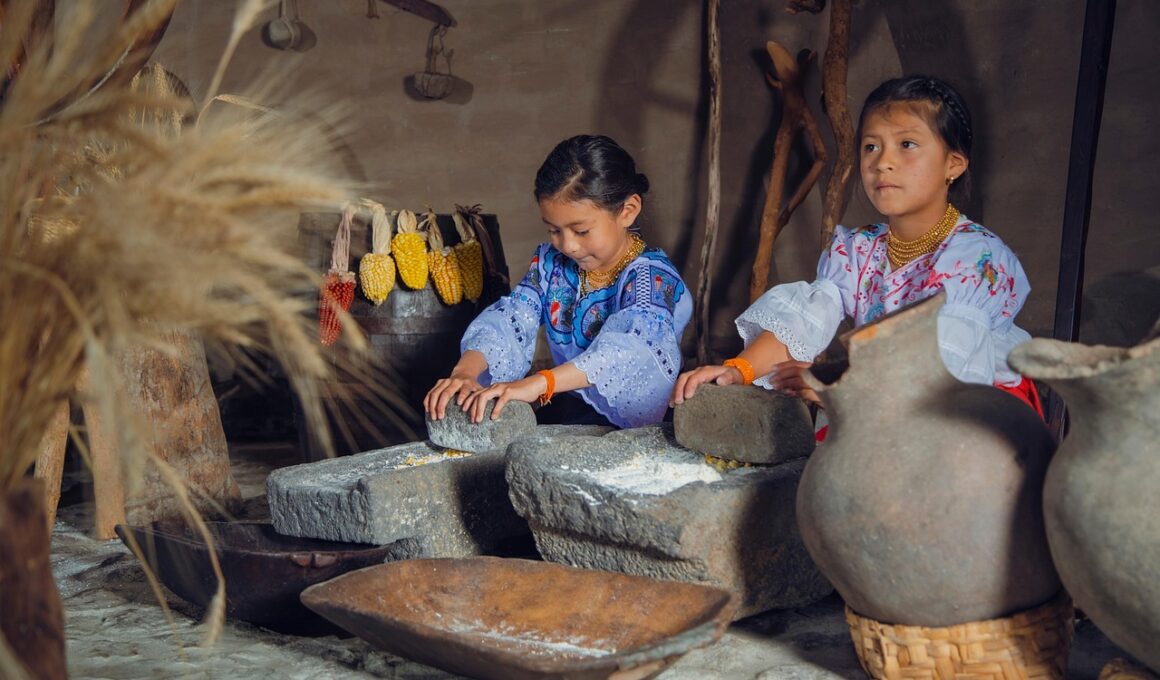
Cultural dimensions such as collectivism and individualism significantly impact how the reciprocity principle is perceived and enacted. In collectivist societies, people prioritize group harmony and social ties. Here, the reciprocity principle is often embedded in the social fabric, leading to expectations of mutual support within communities. Marketers can leverage this by creating campaigns that emphasize community involvement and collective benefits. On the other hand, in individualistic cultures, reciprocity may appear more transactional. Marketing strategies in these regions might focus on personal benefits and rewards, emphasizing direct returns for favors given. The challenge for marketers is to strike a balance between these cultural dimensions. Personalized marketing approaches work well in individualistic cultures, while community-focused efforts resonate more strongly in collectivist contexts. For instance, businesses targeting individualistic societies could employ referral bonuses, while those reaching collectivist audiences might consider group discounts. Understanding these dimensions aids in more precisely targeting marketing efforts for specific regions, enhancing consumer engagement. Ultimately, successfully navigating these cultural differences in reciprocity leads to stronger brand loyalty and market penetration.
Communication styles across cultures also influence how the reciprocity principle is perceived and enacted in marketing contexts. In cultures with high-context communication, much of the message is derived from the surrounding context rather than explicit verbal information. In these environments, subtler gestures of reciprocity are appreciated, which can sometimes lead to challenges for marketers. They must ensure that the intended message is understood within the cultural framework. Conversely, in low-context cultures, messages are more direct, and promotions are often clearly laid out. Here, consumers readily recognize the context of reciprocity in marketing tactics. Marketers operating in high-context cultures can benefit by incorporating indirect ways to imply reciprocity. This could involve storytelling or cultural references that resonate deeply with the target audience. In contrast, direct promotions and transparent offers are more effective in low-context scenarios. For instance, a direct discount offer works well in a low-context culture, while a culturally rich story around a product’s benefit appeals more in high-context settings. Thus, awareness of communication styles is essential for effective strategy formulation.
The Role of Trust in Reciprocity
Trust serves as a foundational element that amplifies the reciprocity principle, impacting various marketing strategies across different cultures. In societies where trust in interpersonal relationships is high, consumers show more willingness to reciprocate offers and favors. Here, marketers can effectively utilize the reciprocity principle through relationship building and customer engagement initiatives. Conversely, in cultures characterized by skepticism or low trust, achieving reciprocity is challenging. In these cases, marketers must work harder to establish credibility and trustworthiness. This can involve showcasing testimonials, user-generated content, and transparent communication practices. Brands must earn this trust before recipients feel comfortable reciprocating in response to promotional offers. For example, a brand in a high-trust society might successfully implement loyalty programs that rely on the reciprocity principle. In lower-trust cultures, they may need to offer more substantial incentives initially to encourage reciprocal behavior. Recognizing these trust dynamics allows marketers to tailor their approaches effectively. Thus, understanding local trust levels is imperative in orchestrating successful reciprocity-driven campaigns.
Social norms also significantly shape the reciprocation process, influencing how marketing strategies are perceived internationally. In cultures with strong social obligations, such as in many Asian societies, reciprocation may be viewed as a moral responsibility. Here, consumers might engage in transactions with brands they perceive as enhancing their social standing or contributing positively to communal welfare. On the other hand, Western cultures often prioritize personal gain; thus, marketing messages must concentrate heavily on individual benefits. An effective approach in collectivist societies can involve highlighting a company’s commitment to social causes, fostering a sense of shared values. For example, marketing initiatives that support local charities might resonate strongly with consumers who prioritize community involvement. In individualistic cultures, leveraging exclusivity or personalized offerings may motivate customers to reciprocate. Marketers must navigate these social norms judiciously to appropriately structure their campaigns, aligning messaging with core values held by their target audiences. As such, examining the social fabric within different cultural contexts is vital for enhancing the effectiveness of reciprocity strategies.
Furthermore, the emotional aspect of reciprocity varies across cultures, affecting how marketing messages are received. In emotional cultures, displays of gratitude and acknowledgment significantly drive reciprocative actions. In these cases, marketers can enhance their campaigns by emphasizing emotional storytelling that appeals to consumer sentiments. Techniques such as emotional branding or community engagement can foster connections that encourage reciprocation. In contrast, cultures with a more pragmatic approach to communication may respond better to logical appeals, focusing primarily on benefits rather than feelings. For example, a brand in an emotional market might highlight personal stories from beneficiaries, creating a narrative that encourages reciprocity. In pragmatic counterparts, a straightforward message about product advantages can be more effective. These emotional dynamics highlight the need for sensitivity and adaptability in marketing strategies across regions. Marketers aiming for success must incorporate emotional cues effectively within their campaigns, aligning them with specific cultural emotional frameworks. Thus, addressing emotional responses can significantly impact the overall efficacy of reciprocity principles in different marketing strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding cultural influences on the reciprocity principle in marketing is essential for creating effective campaigns. The interplay of cultural values, communication styles, trust levels, and emotional aspects profoundly impacts consumer behavior across different regions. By comprehensively grasping these factors, marketers can tailor their approaches to resonate with diverse audiences. This ensures not only a higher response rate but also fosters lasting relationships with consumers. Incorporating cultural diversity into marketing strategies can lead to impactful results, fostering brand loyalty and an enhanced customer experience. A deep respect for cultural nuances when employing the reciprocity principle positions brands favorably in global markets. As businesses continue navigating an increasingly interconnected world, cultural competency will emerge as a significant competitive advantage. Brands that remain adaptable and culturally aware will likely thrive. In this dynamic landscape, those who prioritize understanding and respecting cultural differences in reciprocity principles will build stronger connections with their audiences. Ultimately, cultural intelligence becomes not just an asset, but a necessity in today’s global marketing ecosystem.
Through this understanding, companies can optimize their marketing efforts, ensuring that they resonate effectively with their respective audiences. Exploring the complexities of cultural influence on reciprocity ultimately leads to more robust marketing strategies that can successfully transcend cultural barriers. Marketers must remain vigilant and adaptable, continuously seeking insights that inform their understanding of consumer behavior across diverse cultural landscapes. Whether deploying targeted social campaigns or creating rich emotional narratives, embracing cultural differences within reciprocity principles opens doors to fruitful customer relationships. The essence of successful marketing lies in recognizing the deep-rooted cultural aspects that drive consumer behavior. Attention to these aspects not only informs practical strategy but also drives richer, value-based connections. Hence, the reciprocity principle is not merely a psychological tool but a dynamic relationship-building framework that can be adapted to various cultural standards. Marketers who effectively leverage these insights will find themselves in ideal positions to cultivate deeper, long-term customer interactions. As cultural appreciation in marketing becomes ever more essential, the efficacy of reciprocity reflects its vital role in global outreach and customer loyalty.